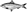
Creature Profile
The rainbow parrotfish is a large fish found in the western Atlantic ocean, from Florida, Bermuda and the Bahamas to Argentina. Males grow up to 3.94 feet long. As their name suggests, rainbow parrotfish are attractively colored with deep green bodies, orange fins, and streaks of green extending outward toward the back and tail. Males are more brightly colored than females but only when fully grown. Because of their unusual mouthparts, they are called parrotfish. The teeth are fused, forming a tough parrot-like beak. The beak is used to scrape algae and other organic matter from the surface of coral.
Rainbow parrotfish can be found on coral reefs as deep as 25 meters, and at night they hide in crevices. They are very social and have been observed in schools of around 40 individuals. The schools graze over the reef much like a herd of cattle over a grassy field. Large amount of calcareous materials are consumed by the schools, and in just one year, one parrotfish can convert a ton of coral into sand. One adult male (called the "supermale") often leads these schools. Parrotfish are able to change sex. That is females if needed may become males in order to reproduce. The supermales are typically sex-reversed females and are strongly territorial, habitually driving other males from their areas. Juveniles have been observed in mangroves adjacent to the reef. These mangroves act as important nursery areas and also provide food-rich, predator free safe-havens for the growing young.
This creature is considered vulnerable due to loss of its mangrove nursery habitat. Since the young parrotfish depend on the nurseries, removal of the mangroves has resulted in decline. Other threats include pollution, over-fishing, and coastal development. To preserve the species, a number of reef have been established as reserves (where fishing and other human pressures are prevented).
Wikipedia Article

|
Wikipedia Article Copyright Notice: This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Rainbow parrotfish". |
May 11, 2017
Glenn, C. R. 2006. "Earth's Endangered Creatures - Rainbow Parrotfish Facts" (Online). Accessed 4/17/2024 at http://earthsendangered.com/profile.asp?sp=12922&ID=5.
Need more Rainbow Parrotfish facts?




